Infectious Disease Programs

Infectious Disease Programs: Combating Global Health Threats
Infectious diseases remain a major public health challenge worldwide, posing significant threats to individuals and communities. Programs focused on combating infectious diseases are critical for preventing outbreaks, controlling the spread of illnesses, and ultimately saving lives. These initiatives involve a collaborative approach, integrating research, prevention, treatment, and education.
Understanding Infectious Diseases
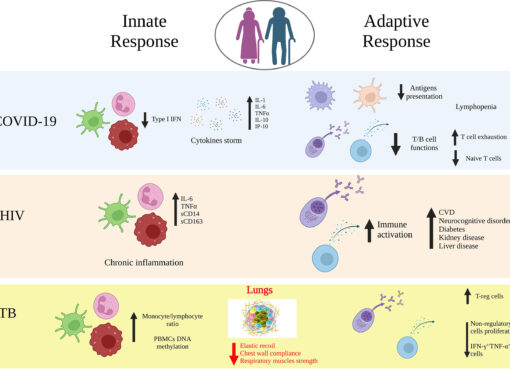
Infectious diseases are caused by pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. They can spread through various means, including person-to-person contact, contaminated food or water, and insect vectors. Common examples include malaria, tuberculosis, HIV/AIDS, and influenza. Addressing these diseases requires targeted strategies tailored to their unique modes of transmission and impact.
Importance of Infectious Disease Programs
Programs aimed at controlling infectious diseases are essential for several reasons:
- Preventing Outbreaks: Early detection and intervention can stop diseases from spreading and becoming epidemics or pandemics.
- Protecting Vulnerable Populations: Certain groups, such as children, the elderly, and those with compromised immune systems, are at higher risk of severe outcomes from infectious diseases.
- Promoting Economic Stability: Disease outbreaks can disrupt economies by straining healthcare systems and reducing workforce productivity.
- Enhancing Global Security: Controlling infectious diseases prevents cross-border transmission and reduces the risk of international health emergencies.
Types of Infectious Disease Programs
There are various programs designed to address specific diseases and broader public health challenges. These include:
1. Vaccination Programs
Vaccines are one of the most effective tools for preventing infectious diseases. Immunization initiatives, such as those led by Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance, aim to provide access to life-saving vaccines in low-income countries.
2. Disease Surveillance and Monitoring
Programs like the Global Influenza Surveillance and Response System (GISRS) monitor the spread of infectious diseases, enabling timely responses to emerging threats.
3. HIV/AIDS Prevention and Treatment
Efforts such as the U.S. President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) focus on reducing new infections, providing antiretroviral therapy, and supporting affected communities.
4. Malaria Control Initiatives
Programs such as the Roll Back Malaria Partnership distribute insecticide-treated bed nets, support research, and improve access to effective treatments.
5. Tuberculosis Eradication Programs
The World Health Organization’s End TB Strategy aims to reduce tuberculosis incidence through early diagnosis, treatment, and preventive care.
6. Zoonotic Disease Control
These programs focus on diseases transmitted from animals to humans, such as rabies and avian influenza, emphasizing the importance of a One Health approach.
Key Organizations in Infectious Disease Control
Several organizations lead efforts in combating infectious diseases, including:
- World Health Organization (WHO): The WHO coordinates international responses to infectious diseases and provides technical support to countries. Learn more at WHO.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): The CDC conducts research, develops guidelines, and supports disease prevention programs worldwide.
- Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation: This foundation funds initiatives to combat infectious diseases, particularly in low-resource settings.
Benefits of Infectious Disease Programs
Infectious disease programs offer numerous advantages, such as:
- Reducing Mortality Rates: These programs save lives by preventing and treating diseases effectively.
- Improving Quality of Life: Controlling diseases allows individuals to lead healthier, more productive lives.
- Strengthening Healthcare Systems: Programs often include capacity-building components that enhance the resilience of healthcare systems.
How to Get Involved in Infectious Disease Programs
For those interested in contributing to infectious disease control efforts, consider the following:
- Pursue Relevant Education: Degrees in public health, epidemiology, or microbiology provide a strong foundation.
- Volunteer with Organizations: Many NGOs and global health initiatives offer opportunities to participate in disease prevention programs.
- Engage in Research: Contributing to scientific research can lead to innovative solutions for controlling infectious diseases.
- Advocate for Public Health Policies: Support policies that prioritize funding and resources for infectious disease programs.
Conclusion
Infectious disease programs are vital for protecting global health, reducing mortality, and promoting economic stability. By focusing on prevention, treatment, and education, these initiatives create a safer and healthier world for everyone. Explore opportunities to support or join these efforts and make a meaningful impact on global health challenges.
One thought on “Infectious Disease Programs”
-
Pingback: Global Health and International Programs - Scholarshiptea


Leave a Comment